The cyber security community has seen a constant surge of information stealers in the past few years. Some are sophisticated and widespread, while others are short-lived and designed for quick profit. Stolen information is primarily used for financial gain, either directly benefiting the actor or indirectly by way of selling the stolen data to other criminals. Recently, we stumbled upon a new stealer named Arkanix. This stealer possibly belongs to the short-lived category of stealers which aim for short-term quick financial gains.
Development & distribution
The malware is advertised on Discord and has seen rapid development. The initial version of the malware is Python-based[1]. From our research, the malware is fairly older than a month. However, in this short time, the malware has also been implemented in C++[2]. Distribution appears to happen by spreading the malware on Discord as legitimate tools or online forums.
Website and configuration panel
Creating accounts for the web panel requires an invite code, which is obtained through a Discord chat.
While we could not manage to see all the features made available through the panel, we did manage to get a glimpse of it, which enabled us to get a few insights into what is being offered. The C++ version of the malware is offered as a “Premium” option. Other Premium options include stealing VPN accounts, Steam accounts, screenshots, Wi-Fi credentials, and of course “Support”. The threat actors provide obfuscation for payloads by employing VMProtect.
Python version
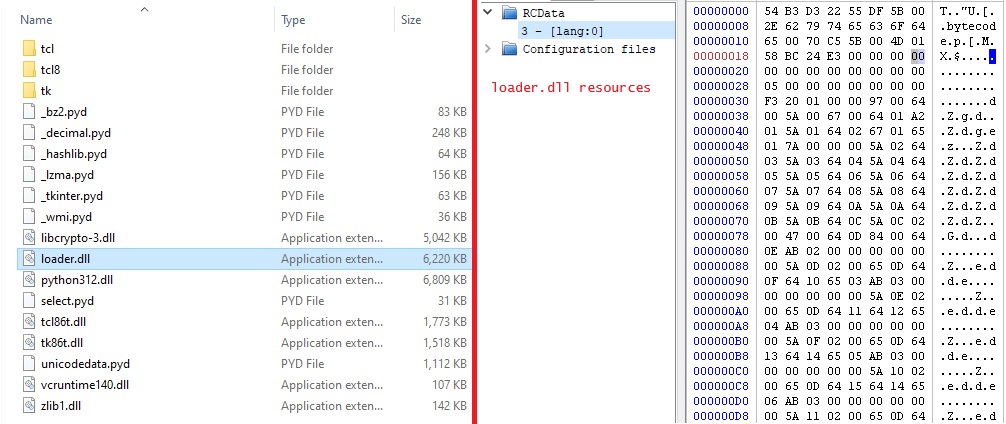
The Python-based version of the malware has been distributed by packaging it via Nuitka, which compiles Python code into byte code. It can generate a self-contained executable which can run without the need for installing additional files. On execution, such files extract a Python environment along with the binary that hosts the compiled Python byte code. The host is able to run the Python byte code with all necessary dependencies. Figure 3 shows the extracted Python environment along with the host of the compiled byte code loader.dll. The image also shows the compiled byte code residing as a resource in loader.dll.
The compiled byte code in this case as the name suggests is only the loader for the actual stealer. The actual malicious code is fetched from hxxps[://]arkanix[.]pw/stealer.py. The fetching succeeds if an appropriate token is set for the HTTP session. The fetched code is run from memory. Examining the code reveals that the stealer has elaborate functionality. “Features” are configured at build time and they are options to control what data is collected. Configurable features are - collecting system information, browser history, browser autofill information, VPN data, steam accounts, screenshots, telegram data, and enabling self-spreading via Discord.
Stealing capabilities
The malware supports collecting information from a variety of Chromium-based browsers, popular ones being Edge, Chrome, Opera, Vivaldi, Tor, Yandex etc. Collects data from a long list of browser extensions, most of them being Crypto/Wallet related. Some examples include ExodusWeb3, MetaMask, Binance, Oxygen, etc.
Wallet data from Exodus, Electrum, Etherium and a few others are also stolen. The stealer searches Desktop, Documents and Downloads folders for files with pre-configured extensions and containing certain keywords in their names. The malware then uploads files such found to the malicious server asynchronously while the rest of the stealing activity continues. Additional payload is fetched for collecting Chrome data. Discord tokens are stolen and if self-spreading is enabled, the malware sends itself to people in the contact list and in various channels.
System information collected includes operating system version, CPU and GPU information, memory capacity, screen resolution, keyboard layout, time zone information and installed Antivirus software. Browser history, Autofill information and stored credit card information is collected. Wi-Fi profiles are dumped by use of the ‘netsh wlan show profiles’ command. Clear test Wi-Fi passwords are stolen that way (via key=clear command line option for each profile available). VPN data from Mullvad, NordVPN, ExpressVPN and ProtonVPN are collected. Collected files are data are submitted to the malicious server via the route hxxps[://arkanix[.]pw/delivery. Additionally, an extra collector payload is fetched from the remote server and executed. The malicious server is not available at the time of writing this article and therefore, additional payloads could not be fetched for analysis.
C++ Version
The native code version of the malware is functionally very similar. However, the native version employs a different trick for stealing credentials and cookies stored in Chromium based browsers. Chrome introduced ABE (App Bound Encryption) in version 127. App-Bound Encryption uses a trusted background service to confirm which application is requesting data encryption. This service then bakes the app's unique identity into the resulting encrypted data. When decryption is later requested, the service checks the data's embedded identity against the identity of the current requesting app. Decryption fails unless the two identities are an exact match, effectively preventing data from being shared or stolen by other applications on the system. More information on ABE can be found in this blog post from Google.
To defeat ABE, the native version of the stealer, employs ‘Chrome Elevator’ a post exploitation tool which uses process injection to inject a binary into the Chrome process and lets the injected code dump Chrome data by running in the context of the browser and thereby bypassing the ABE hurdle. The tool is stored in the binary as a PE resource and is extracted and run from the %TEMP% folder. Chrome Extractor is able to extract data from both Edge, Chrome and Brave browsers.
The native version of the malware can additionally harvest RDP information from ‘.RDP’ files. However, unlike the Python version, the Discord self-spreading functionality is missing in the binary we examined.
The collected info is submitted to the route hxxps://arkanix[.pw]/api/upload/direct. The user agent for the request is set to ‘ArkanixStealer/2.0’.
Closing Remarks
It seems remarkably easy to start an online community and get a crime business going to earn quick bucks. The fact that in a short time span the actors can deliver different malware payloads coded in different languages fluidly hints at the fact that these actors have considerable experience in running such a crime scheme.
IOCs
1. 6ea644285d7d24e09689ef46a9e131483b6763bc14f336060afaeffe37e4beb5 – Python based version
2. 6960d27fea1f5b28565cd240977b531cc8a195188fc81fa24c924da4f59a1389 – Native code version
https[://]arkanix[.]pw